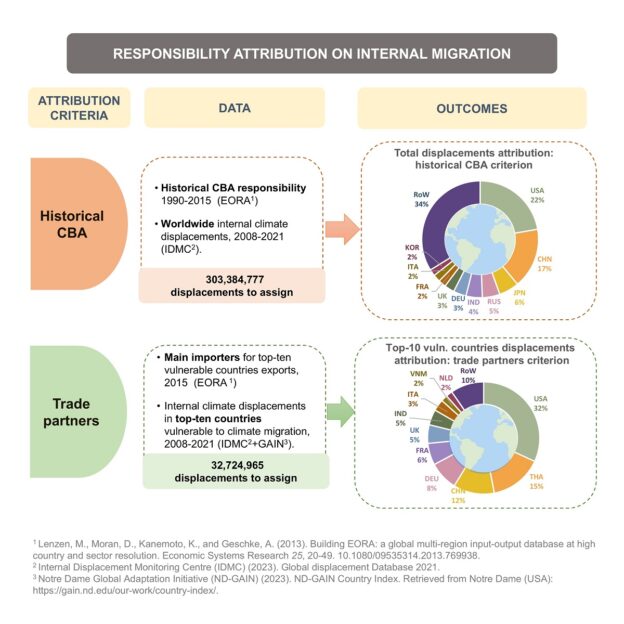
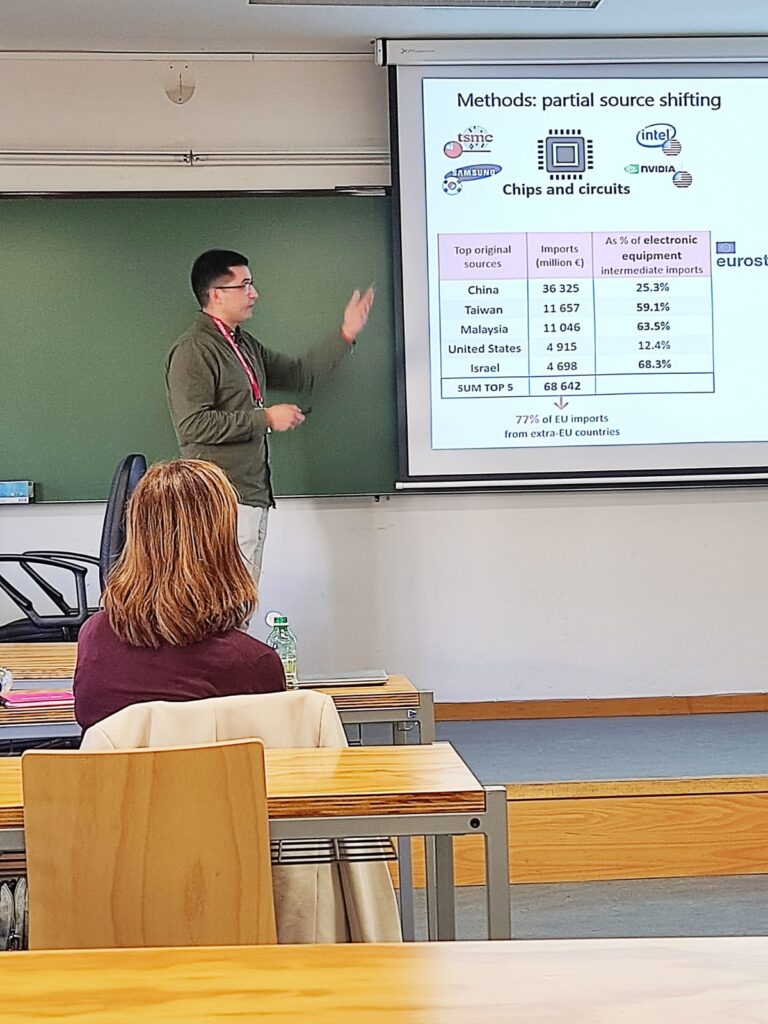
The GEAR members Luis A. López, Mateo Ortiz, Ángela García-Alaminos and María Ángeles Cadarso have recently published the paper entitled “Consequences of Legislation-based Reshoring for EU Carbon Emissions in Global Value Chains» as a part of the special issue titled “Industrial Policy and Global Value Chains in an Era of Disruptions” in the Journal of International Business Policy.The article is a result of the European Commission under Horizon Europe project TWIN SEEDS (Towards a World Integrated and Socio-economically Balanced European Economic Development Scenario), grant number 101056793 (https://doi. org/10.3030/101056793).
The recent global events, including the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical shifts, have emphasized the fragility of global value chains (GVCs) and sparked interest in reshoring strategies. These strategies involve relocating production closer to home or to allied countries to enhance resilience. However, the environmental implications of such moves remain underexplored. Now, in the article “Consequences of Legislation-based Reshoring for EU Carbon Emissions in Global Value Chains», we investigate how reshoring driven by EU regulations impacts CO2 emissions across GVCs, focusing on strategic products like antibiotics and semiconductors.
The study employs an environmentally extended multiregional input-output model combined with a source-shifting technique to assess the effects of reshoring on the EU’s carbon footprint. It analyzes several scenarios involving trade reconfigurations for strategic products identified by the European Commission. This approach allows to evaluate the environmental impacts of shifting production locations and identify potential synergies between resilience and sustainability goals.
The results indicate that reshoring can lead to significant reductions in the EU’s carbon footprint, particularly for carbon-intensive sectors like iron and steel. While direct emissions within the EU may increase, the overall carbon footprint decreases due to lower emissions from new suppliers compared to former ones. This study concludes that strategic reshoring can align with climate goals, offering a pathway to enhance both resilience and sustainability. Future implications suggest that coordinated policies could further optimize these benefits, supporting the EU’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions while strengthening supply chain resilience.
You can find the full text here: https://doi.org/10.1057/s42214-025-00216-8