The goal of the analysis layer metamodels is the definition of a language to describe the high-level features of Context Aware Applications (CAAs) for Ubiquitous Computing Environments (UCEs) defined in [1]. The key concepts of the analysis layer are: the entity, the space and the task.
The relationship among them defines the following paradigm to build analysis layer models.
A CAA for UCE is defined by a set of entities that perform tasks within a space
Therefore, 3 metamodels were defined:
- The Social metamodel (SoMM) to describe the relationship among entities in terms of social instances (roles, individuals, etc.)
- The Space metamodel (SpMM) to define the relationship among physical or vitual spaces.
- The Task metamodel (TaMM) to define how entity characteristics are related to tasks and spaces
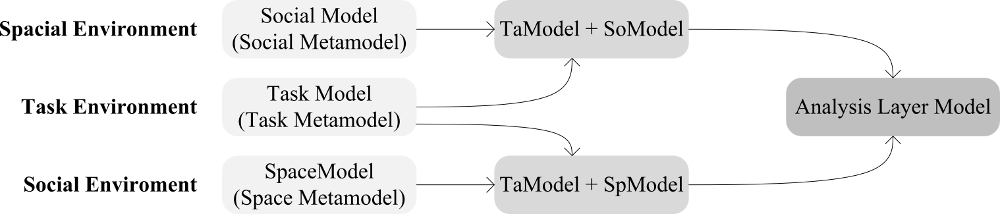
The relationship among the models conforming these metamodels is depicted in Figure 2.
References
[1] Albrecht Schmidt, Michael Beigl, and Hans-Werner Gellersen. There is more to context than location. Computers & Graphics, 23(6):893-901, 1999.
You can reference this work as:
Ricardo Tesoriero, José A. Gallud, María D. Lozano and Víctor M. R. Penichet. CAUCE: Model-driven Development of Context-aware Applications for Ubiquitous Computing Environments. Journal of Universal Computer Science, Vol. 16, No. 15, pp. 2111-2138. 2010. Link: http://www.jucs.org/jucs_16_15/cauce_model_driven_development