Research Lines

Serious Games for Health
Video games and interactive applications with diagnosis and treatment purposes
Recent research lines aim to apply neuroscience to the design of serious video games for health purposes. We use qualitative physiological measures through EEG, eye-tracking and biomedical devices to evaluate cognitive skills during the use of video games, virtual avatars and VR experiences.

Assistive Technologies
ITCs solutions for people with special needs and older adults
I have been working on adapting environmental sensors for behavior and activity recognition to early diagnosis and treatment of psychological issues. The research contributions in this area have been applied to e-health and ambient assisted living projects.
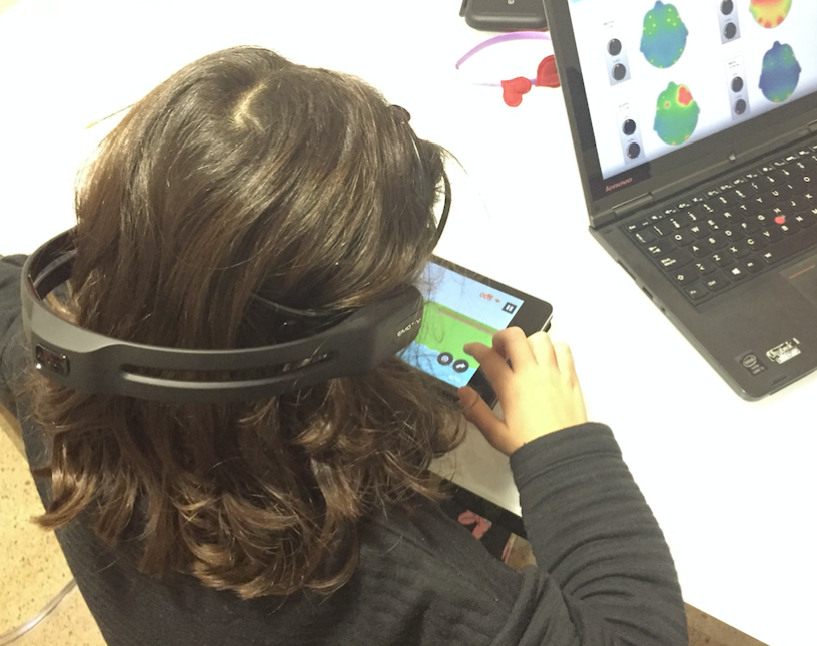

Health Monitoring and Diagnosis
Ubiquitous and mobile solutions for health purposes
Solutions for efficiently managing patient medical records in healthcare environments, monitoring vital signs, supporting obesity,rehabilitation and frailty aspects by means of mobile and IoT-based approaches and, everyday monitoring solution to analyze activities, behaviour and gait.
Interests
- Neurosciences
- Affective Computing
- Ambient Intelligence
- Cognitive Computing
- Ubiquitous Computing
- Intelligent Interfaces
April 2009
Context Modelling for Information Visualization into Intelligent Environments

Author: Ramón Hervás Lucas
Advisor: Prof. José Bravo Rodríguez
This dissertation presents an infrastructure that contributes to ubiquitous information. Advances in Ambient Intelligence may help to provide us with the right information at the right time, in an appropriate manner and through the most suitable device for each situation. It is therefore crucial for such devices to have contextual information; that is, to know the person or persons in need of information, the environment, and the available devices and services. All of this information, in appropriate models, can provide a simplified view of the real world and let the system act more like a human and, consequently, more intelligently. A suitable context model is not enough; proactive user interface adaptation is necessary to offer personalized information to the user. In this Ph.D Thesis, we present mechanisms for the management of contextual information, reasoning techniques and adaptable user interfaces to support visualization services, providing functionality to make decisions about what and how available information can be offered. Additionally, we present the ViMos framework, an infrastructure to generate context-powered information visualization services dynamically.
October 2010
Ambient Intelligence Modeling: A context-aware environment through tagging

Author: Salvador W. Nava Díaz
Supervisor: Prof. José Bravo Rodríguez and Prof. Ramón Hervás Lucas
This thesis deals with the proposal of a framework and an architecture that allow the design and modeling of environments able to perceive the context-awareness through tagging. In this proposal, we have carried out an analysis of the domain related with the context-awareness. Thus, we have defined the relevant entities of the environment such as areas, devices, objects and users, as well as the contextual information acquired from the actions performed with these entities. In this way, the architecture can support and provide (implicit) adaptive services, not only to the user interacting with the entities in a certain moment, but also to other users; these users can receive context-awareness services subsequently, in a proactive way. On the other hand, the model includes a grammar to represent the dynamic behavior of the environment, a classification of the interactions, and mechanisms to implement the context-awareness services by means of tagging.
This Ph.D. Thesis aims to provide a model for taking advantage of the actions carried out by the users and, in consequence, offer better services in an implicit way, helping in the development of user’s activities. Basically, these characteristics are activated by means of the link of contextual information with relevant entities of the environment, and by mechanisms to give the needed support for generating context-awareness services through tagging. Thus, the effort made by the users is reduced considerably.
July 2012
Framework for Patient Mobile Monitoring

Author: Vladimir Villarreal Contreras
Supervisor: Prof. José Bravo Rodríguez and Prof. Ramón Hervás Lucas
This thesis has been developed with the purpose of offering technological solutions that allow patients improved and timelier follow-up and control of their disease, offering constant and timely responses. A conceptual framework called «MoMo» (Mobile Monitoring) allows for the development of parameterized mobile applications. This is conducive to medical tracking through mobile devices, which are in daily use by the patient, and biometric devices that currently offer high technological performance.
The applications based on the framework are generic, adaptable, remote and mobile. Generic, because they allow for the development of applications for multiple diseases following the conceptual design of the developed framework. Adaptable, because they offer services tailored to each type of disease and personalize the user’s characteristics, making the interaction more transparent. Remote, because the medical staff can be aware of data obtained by the patient biometric devices through the mobile device in a non-intrusive manner. Mobile, because development is based on the integration of small size, portable and wireless devices. These applications provide greater autonomy for the patient.
January 2014
Mobile system for detection and assessment of frailty syndrome in elderly people

Author: Jesús Fontecha Diezma
Supervisor: Prof. José Bravo Rodríguez and Prof. Ramón Hervás Lucas
This doctoral thesis proposes a system for supporting physicians and geriatricians in frailty detection and diagnosis, by using smartphones and accelerometer sensors in combination with a set of clinical parameters associated with fragility. In addition to developing the system, this work also presents the methods and procedures needed to set up several aspects of frailty assessment in ubiquitous and healthcare environments, by using a service-based approach.
Applying classification mechanisms and similarity algorithms as part of the assessment, is another contribution of this work, taking into account the difficulty of a comprehensive assessment of frailty nowadays. Similarly, a mobile application has been developed to provide the geriatrician a tool which encourages the visualization and interpretation of frailty results facilitating the clinical decision-making.
July 2020
Cognitive Variables for the Design of Serious Games for Health: A Study with EEG and Eye Tracking

Ph.D Candidate: Tania Mondéjar Palomares M.Sc
Advisor: Ramón Hervás Lucas Ph.D & José Miguel Latorre Postigo Ph.D
Nowadays, we are living a different use and understanding of videogames. Particularly, Serious Games aim to develop specific objectives beyond entertainment, mainly, educational and training objectives. There is a novel perspective that uses Serious Games as an innovative tool in the field of health (health games).
This thesis belongs to that perspective due to its multidisciplinary approach focused on neurosciences and computation. The main goal is to determine the neuropsychological brain functions while using videogames to help the design of serious games with health purposes, particularly, to support the diagnosis and treatment of cognitive-related pathologies
October 2021
Modeling Human-Agent Interaction based on Affective and Cognitive Computing

Ph.D Candidate: Esperanza Johnson Ruiz
Advisor: Ramón Hervás Lucas Ph.D
With a certain percentage of the population having been diagnosed with different forms of Social Communications Disorders (SCD), current assistive technologies can improve their quality of life. In this thesis we explore the way in to approach an assistive system for improving SCD, based on human-avatar interaction.
This thesis will contribute with a general methodology that develops different kinds of interaction between humans and avatars, including the relationship among them and their communication skills. These skills are typically training to treat SCD.
Ongoing 2021
Behaviour-Aware Computing through Activity Recognition, Context-Awareness and Psychological Foundations

Ph.D Candidate: Carlos Gutierrez López de la Franca.
Advisor: Ramon Hervás Lucas Ph.D
Activity Recognition in a scientific setting is a field that is extremely popular, in which numerous and diverse proposals exist and tackle the creation of systems capable of recognising activities through different types of sensors.
Therefore, with this proposal we intend to analyse the Behaviourof people, with a focus not only based on Activity Recognition but also with a strong component centred on smart environments with context awareness and supported by the foundations of the Psychology of Behaviour.
Ongoing 2022
Cognitive analysis and training through interactive applications

Ph.D Candidate: Luis Cabañero Gómez.
Advisor: Ramon Hervás Lucas Ph.D
Advisor: Iván González Díaz Ph.D
This doctoral thesis will study how to design interactive applications that induce cognitive improvement of users. To do this it will be necessary to evaluate the cognitive state using Electroencephalography (EEG), a non-intrusive technique that arises in a medical context that allows to measure the electrical potential generated by the brain. During the thesis it will be studied and it will be determined which computational EEG techniques allow demonstrating cognitive improvement after the prolonged use of interactive applications. From these findings it will be possible to establish design principles of interactive applications that improve specific cognitive skills.
Colleagues

Tania Mondéjar
CEO eSmile Psychology

Jesús Fontecha
Postdoc Researcher

José Bravo
MAmI Research PI

Iván González
Postdoc Researcher
Research Projects
2019-2021
(IP) M4S: Mobile-computing-based Multitasking for Mild cognitive impairment Monitoring and early Screening
Retos de Investigación – Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
2016-2017
DIMO: A smart system for Diabetes Mellitus monitoring

Fundación MAPFRE. Ayudas a la investigación de Ignacio H. de Larramendi.
2014-2017
(IP) FRASE: Frailty and dementia characterization through gait analysis

Financed by Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia. CICYTTIN2013-47152-C3-1-R
2013-2016
UbiHealth: Exchange of excellence in ubiquitous computing technologies to address healthcare challenges

Marie Curie European Project REF 316337
http://www.ubihealth-project.eu/
2013-2015
PIA: Personal IADL Assistant.

Financed by European Union. AAL Joint Programme (Call 5)
2011-2013
TALISMAN+: Intelligent system for follow-up and promotion of personal autonomy
Financed by Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia. CICYT TIN2010-20510-C04-04
2010-2012
Ambient Intelligence in an educational context: A proposal for NFC technological adaptability in nursing care training
CLM Regional Project.
2009-2010
Ambient Intelligence for supporting chronic diseases: A proposal for diabetes care
CLM Regional project
2008-2010
ALIADO. Alzheimer Intelligent Ambient Domotic System
Financed Work – Ministerio de Industria FIT-350300-2007-86.
2009-2010
NFC Adaptability for Dependency
Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha PII2I09-0127-2321
2007-2008
AmITACA. Ambient Intelligence Technologies and Applications for Context Awareness
CCNT Company UCTR070023
Research Stays
Panama
2018
Technological University of Panama
Contact. Prof. Vladimir Villarreal PhD
Chile
2014
University of Chile
Contact. Prof. Sergio Ochoa PhD
Mexico
2013
CICESE
Contact: Prof. Jesús Favela PhD
U.K.
2010
Ulster University
Contact: Profs. Chris Nugent and Luke Chen
Mexico
2009
University of Tamaulipas
Contact: Prof. Gabriel Chavira PhD
Other Research Activities
Doctoral Panel
Gabriel Chavira, PhD. (2009). Ambient Intelligence Modeling through Touch Interaction.
To do
Editorial Board Member
Recent Patents on Telecommunications (Member of the Editorial Board)
International Journal of Ubiquitous Computing (Member of the Editorial Board)
MDPI Sensors (Guess Editor)
Ambient Intelligence & Humanized Computing (Guess Editor)
Journal of Universal Computer Science (Guess Editor)
Interacting with Computers (Guess Editor). Special Issue on Context-Driven Human Environment Interaction (CdH-E Interaction). https://doi.org/10.1093/iwc/iwt063
Journal of Computer Systems, Science & Engineering (Guess Editor). Special Issue on New holistic trends in ambient intelligence
Program Committee Member
Please, see section Experiences for information about Conference Organization
To Do
Reviewer (Selection)
To Do
Research and Knowledge Transfer
[Spin-Off] Founding partner of the Spin-Off AmIRIA Solutions S.L., associated to the University of Castilla – La Mancha, (2010-2016)
[Transfer Project] Intelligent mobile system for the comprehensive, personalised and continuous monitoring of patients with Diabetes Mellitus. MAPFRE Foundation. January-December 2015.
[Contract] Transfer of software product for the automation of business processes through RFID to the company Dinfor S.A.
[Contract] Consultancy services specialized in aspects related to the research areas of the group through the company AmIRIA Solutions.